字典树
字典树
例题1
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树) - 力扣(LeetCode)
Trie(发音类似 “try”)或者说 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补全和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie()初始化前缀树对象。void insert(String word)向前缀树中插入字符串word。boolean search(String word)如果字符串word在前缀树中,返回true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回false。boolean startsWith(String prefix)如果之前已经插入的字符串word的前缀之一为prefix,返回true;否则,返回false。
自己想的最简单的方法(但并不是真正的字典树)
class Trie {
Set<String> set;
public Trie() {
this.set = new HashSet<>();
}
public void insert(String word) {
set.add(word);
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return set.contains(word);
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
for(String word : set){
if(word.startsWith(prefix)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
insert 操作
- 遍历字符串
word,同时用变量cur表示当前在 26 叉树的哪个节点,初始值为root。 - 如果
word[i]不是cur的儿子:- 创建一个新的节点
node作为cur的儿子。 - 若
word[i] = 'a',将node记录到cur.son[0]。 - 若
word[i] = 'b',将node记录到cur.son[1],依此类推。
- 创建一个新的节点
- 更新
cur为儿子列表中的相应节点。 - 遍历结束,将
cur.end标记为true。
search 和 startsWith
这两个方法可以复用同一个函数 find:
find 实现
- 遍历字符串
word,同时用变量cur表示当前在 26 叉树的哪个节点,初始值为root。 - 如果
word[i]不是cur的儿子:- 返回
0。 search和startsWith收到0后返回false。
- 返回
- 更新
cur为儿子列表中的相应节点。 - 遍历结束:
- 如果
cur.end是false,返回1(表示前缀匹配但不是完整单词)。 - 如果
cur.end是true,返回2(表示完全匹配单词)。
- 如果
结果判断
search:收到2返回true,否则返回false。startsWith:收到非0返回true,否则返回false。
class Trie {
private static class Node {
boolean end = false;
Node[] son = new Node[26];
}
Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
public void insert(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[i] == null) {
cur.son[i] = new Node();
}
//进入下一层
cur = cur.son[i];
}
//字符串树最后一层
cur.end = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return find(word) == 2;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return find(prefix) != 0;
}
int find(String word) {
Node cur = root;
//遍历二十六叉树
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[i] == null) {
return 0;
}
cur = cur.son[i];
}
// 走过同样的路(2=完全匹配,1=前缀匹配)
return cur.end ? 2 : 1;
}
}
例题2
211. 添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计 - 力扣(LeetCode)
请你设计一个数据结构,支持 添加新单词 和 查找字符串是否与任何先前添加的字符串匹配 。
实现词典类
WordDictionary:
WordDictionary()初始化词典对象void addWord(word)将word添加到数据结构中,之后可以对它进行匹配bool search(word)如果数据结构中存在字符串与word匹配,则返回true;否则,返回false。word中可能包含一些'.',每个.都可以表示任何一个字母。
'.'要匹配26个字母,所以用递归比较好
class WordDictionary {
class Node {
boolean end = false;
Node[] son = new Node[26];
}
Node root;
public WordDictionary() {
root = new Node();
}
public void addWord(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[i] == null) {
cur.son[i] = new Node();
}
cur = cur.son[i];
}
cur.end = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return dfs(word, 0, root);
}
boolean dfs(String word, int pos, Node node) {
if (pos == word.length()) {
return node.end;
}
char c = word.charAt(pos);
if (c == '.') {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (node.son[i] != null && dfs(word, pos + 1, node.son[i])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} else {
c -= 'a';
if (node.son[c] == null) {
return false;
}
return dfs(word, pos + 1, node.son[c]);
}
}
}
例题3
给定一个
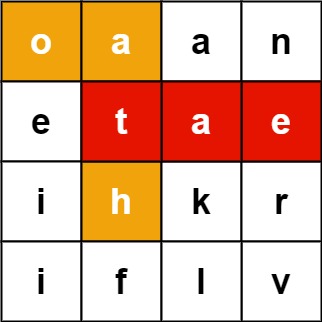
m x n二维字符网格board和一个单词(字符串)列表words, 返回所有二维网格上的单词 。单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"] 输出:["eat","oath"]
思路:字典树+回溯算法
class Solution {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][] visited;
int m, n;
Node root = new Node();
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
visited = new boolean[m][n];
for (String w : words) {
insert(w);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dfs(board, i, j, root, "");
}
}
return res;
}
void dfs(char[][] board, int i, int j, Node node, String path) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= m || j >= n) {
return;
}
if (visited[i][j]) {
return;
}
char c = board[i][j];
if (node.son[c - 'a'] == null) return;
visited[i][j] = true;
node = node.son[c - 'a'];
path += c;
if (node.end) {
res.add(path);
node.end = false;
}
dfs(board, i + 1, j, node, path);
dfs(board, i - 1, j, node, path);
dfs(board, i, j + 1, node, path);
dfs(board, i, j - 1, node, path);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
public void insert(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[i] == null) {
cur.son[i] = new Node();
}
cur = cur.son[i];
}
cur.end = true;
}
static class Node {
boolean end = false;
Node[] son = new Node[26];
}
}
本文是原创文章,采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 协议,完整转载请注明来自 青云小筑
评论
匿名评论
隐私政策
你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果